Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Determining the Current Directory.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated December 7, 2024)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365
If you are programming macros in VBA, it is often helpful to know the directory that Windows feels is the current one. You can find out which directory is current by using the following syntax:
MyDir = CurDir
When this line is executed, MyDir (a string) will be equal to the full path of the current directory.
Understand that the path returned by CurDir is the path that Windows feels is the current directory, not the path that Excel feels is the current directory. In other words, CurDir won't return a path equal to the current path in which you are working with your workbooks. CurDir reflects the directory set using the ChDir command, which is detailed in a different ExcelTip.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (9363) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Determining the Current Directory.

Solve Real Business Problems Master business modeling and analysis techniques with Excel and transform data into bottom-line results. This hands-on, scenario-focused guide shows you how to use the latest Excel tools to integrate data from multiple tables. Check out Microsoft Excel Data Analysis and Business Modeling today!
When creating macros, you often need to process numbers in various ways. VBA allows you to convert a numeric value to an ...
Discover MoreNeed to know the address of the cell that is currently selected? The function and macro highlighted in this tip will come ...
Discover MoreIf you have a series of values in a column, you might have a need to separate the values into even values and odd values. ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2025-01-07 09:58:24
J. Woolley
@Alan
Well maybe it didn't change. If the open workbook is new and hasn't been saved, clicking Browse presents Excel's default path.
2025-01-06 04:41:47
Alan
@J
Indeed it does! It must have changed at some point.
2025-01-03 11:51:49
J. Woolley
@Alan
I didn't realize F12 > Esc would change CurDir to the open workbook's path; thank you for that. But even before changing CurDir, when I use File > Open or Ctrl+O to open another file, clicking Browse (see Figure 1 below) presents the open workbook's path without needing "to go and find it." Alt+F+O+O is an alternative for File > Open > Browse. (I'm using Excel 365.)
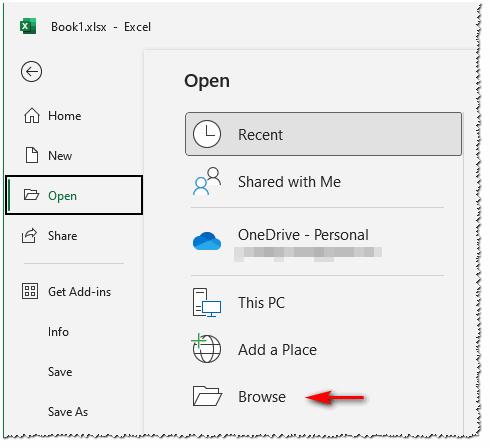
Figure 1.
2025-01-02 09:16:58
Alan
Further to mine below: ...so then if you want to open another file from the same directory, you have to go and find it (the workaround being a quick F12 and Esc to change the default first).
2025-01-02 09:15:06
Alan
One thing I do find really annoying about Excel is that it defaults to the default directory, I wish it would change it to the file's directory (i.e. when opening Excel via the file in Windows Explorer).
2024-12-08 11:53:29
J. Woolley
Here's some additional information related to this Tip based on Windows. Note the difference between a VBA function, which returns a result, and a VBA statement, which does not.
1. CurDir is a VBA function with the following syntax:
CurDir([Drive])
Drive is optional text like "C" or "D" to specify a drive on your computer; default is null text like "" to specify the current drive. Only the first character of Drive applies; any additional characters are ignored. CurDir returns Drive's current path as text (like "C:\Users\Me\Documents").
2. The following expression returns the current drive as text (like "C"):
Left(CurDir(), 1)
This expression produces the same result:
Left(CurDir, 1)
3. The following VBA statement will change the current drive to Drive, which must be text like "C" or "D" identifying a drive on your computer:
ChDrive Drive
Only the first character of Drive applies; any additional characters are ignored. If Drive is null text like "" the current drive is not changed.
4. The following VBA statement will change a drive's current directory (folder) to Path:
ChDir Path
Path must be text like "C:\Windows" or "\Users\Me\Documents" identifying an existing folder. If Path does not specify a drive, the current drive applies; if Path does specify a drive, the current directory on that drive will change. The current drive does not change when Path specifies a different drive. Path can include relative identifiers like ".\" for the current folder or "..\" for its parent folder.
5. The following VBA statement will create a new directory (folder) named Path:
MkDir Path
Path must be text like "C:\Users\Me\Desktop\Office" to create a new folder named Office on your Desktop. If Path does not specify a drive, the current drive applies. The current drive does not change when Path specifies a different drive. Path can include relative identifiers like ".\" for the current folder or "..\" for its parent folder.
6. The following VBA statement will remove an existing directory (folder) named Path:
RmDir Path
Path must be text like "C:\Users\Me\Desktop\Office" to remove an existing folder named Office on your Desktop. If Path does not specify a drive, the current drive applies. The current drive does not change when Path specifies a different drive. Path can include relative identifiers like ".\" for the current folder or "..\" for its parent folder. Path must not specify the current path on the current drive (i.e., CurDir).
7. Dir is a VBA function that returns the volume label of a drive or the name of a file or directory (folder) that matches a specified pattern or attribute.
Dir is well described here: https://trumpexcel.com/vba-dir-function/
8. Here are some Excel properties related to this Tip:
Application.DefaultFilePath is the default path used by Excel when it opens a file (like "C:\Users\Me\Documents").
Application.PathSeparator is the path separator character (like "\").
ActiveWorkbook.Name is the active workbook's name (like "Book1.xlsx").
ActiveWorkbook.FullName is the active workbook's name including its path (like "C:\Users\Me\Documents\Office\Book1.xlsx").
ActiveWorkbook.Path is the complete path of the active workbook's parent folder (like "C:\Users\Me\Documents\Office").
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments