Jan's company recently upgraded to Office 365 ProPlus. With it came a #SPILL! error when using VLOOKUP, which he uses a LOT. He is now unable to use VLOOKUP with a filter. Jan knows it would be easy to sort and/or to remove the #N/A that came from the previous VLOOKUP, but this error is causing him a lot of extra time and effort. He wonders if there is a way to turn this "feature" off.
In the very near past, Microsoft changed how it calculates worksheets. This was a HUGE change, and you may have read about it elsewhere. Here's one article that provides some great information on the change:
https://exceljet.net/dynamic-array-formulas-in-excel
The article is rather long; you'll want to set aside some time to digest the information it contains. If you create lots of formulas in Excel, you'll want to do so, though—the change to the program means you must understand it, eventually.
Essentially, Microsoft did away with the concept of array functions (though they will still work), instead allowing almost all functions, including VLOOKUP, to return an array of values. If the array of returned values won't fit in the available space, you get the new #SPILL! error.
Quite honestly, the answer isn't to disable #SPILL! errors; there really is no way to do so. The answer is to understand what Excel is now doing as it calculates and then modify your formulas accordingly.
Let's look at an example. Let's say you have a worksheet that lists items and their prices in a simple two-column set of data. Then, to the right of this, you enter some items and use a VLOOKUP function to return the prices associated with each of those items. When you open this workbook in an older version of Excel (2019 or earlier) you get great results. (See Figure 1.)
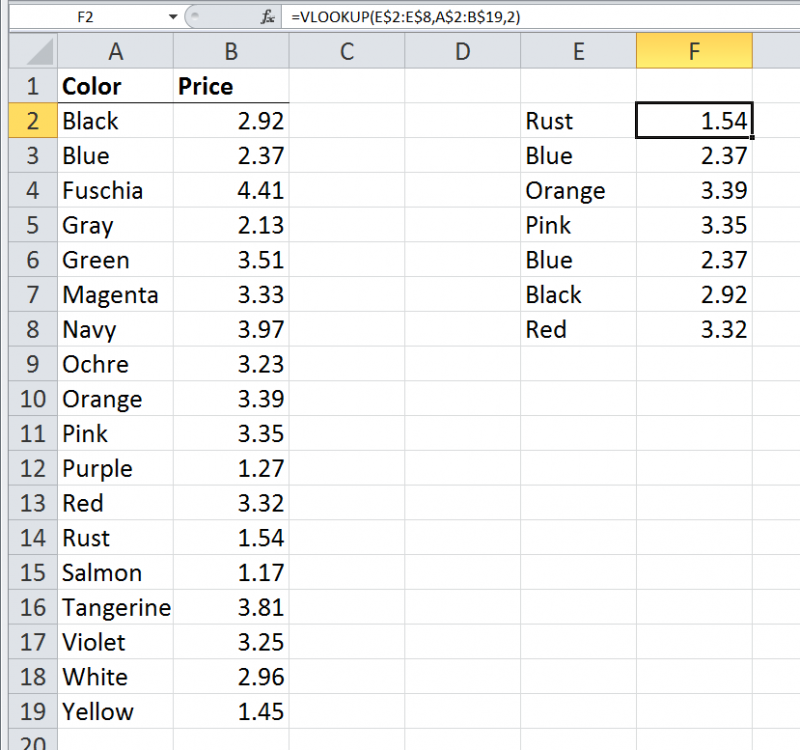
Figure 1. A simple VLOOKUP formula in Excel 2010.
This screen shot was taken using an Excel 2010 system, but it would work the same if you looked at it in Excel 2016 or even Excel 2019. Note in this example that the VLOOKUP formula in cell F2 (shown in the Formula bar because cell F2 is selected) is copied down to the range F2:F8. You get the desired results because the VLOOKUP function returns a single value from the table.
Now, let's look at what happens if you create the same workbook, using the same formulas, in the version of Excel provided with Office 365. In this case you will see errors. (See Figure 2.)
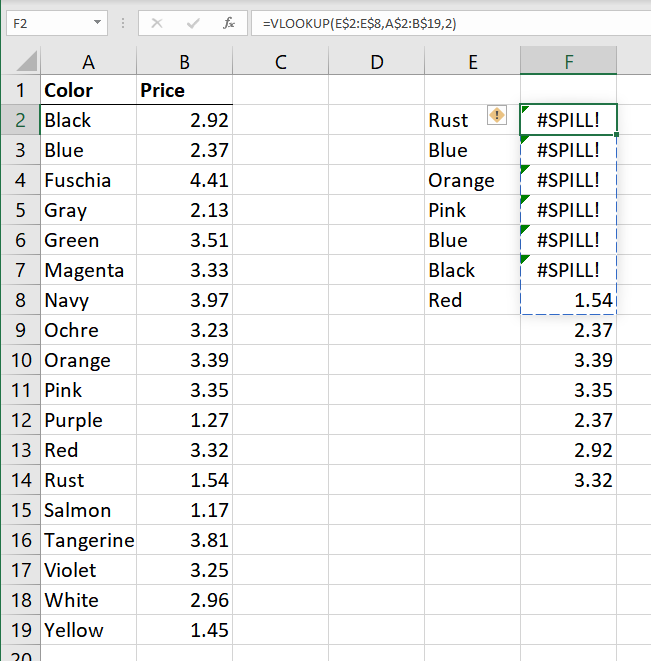
Figure 2. The same simple VLOOKUP formula in the latest version of Excel.
Notice the #SPILL! errors. This error occurs because the VLOOKUP formula can now return more than a single value. In fact, when you use a range of cells in the very first parameter for VLOOKUP, it will now return a value for each cell in that range. Thus, using the range E2:E8 for the first parameter means that VLOOKUP returns 7 values. In other words, it automatically returns an array of values. If those values cannot all be displayed, then you get the #SPILL! error. That is why you are seeing the #SPILL! error in cells F2:F7; there are things below them that stop all the values returned in those formulas from being displayed. You don't see the error in cell F8 because there is nothing below that cell stopping the display.
So, how do you fix this? There are actually three ways you can fix it. In this particular example, the easiest way would be to simply delete everything in cells F3:F8. This allows the formula in cell F2 to "spill" correctly to the rest of the cells below it.
The second approach would be to change the formula in cell F2, so it looks like this:
=VLOOKUP(@E$2:E$8,A$2:B$19,2)
Notice the use of the @ symbol just before the first parameter. This tells Excel that you want the VLOOKUP formula to return just a single value. The other way to adjust the formula would be to make it look like this in cell F2:
=VLOOKUP(E2,A$2:B$19,2)
Now you can copy either formula down from cell F2 into the full range of F2:F8 and you won't have a problem. Why? Because (again) VLOOKUP in these instances is returning only a single value, not an array of values.
The upshot is that the best way to change your formulas is to either (1) make sure there is nothing blocking the display of the full array of values you are requesting VLOOKUP to return or (2) modify the first parameter so that it references just a single cell.
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (13750) applies to Microsoft Excel 2021.

Solve Real Business Problems Master business modeling and analysis techniques with Excel and transform data into bottom-line results. This hands-on, scenario-focused guide shows you how to use the latest Excel tools to integrate data from multiple tables. Check out Microsoft Excel Data Analysis and Business Modeling today!
The MODE function is used to determine the most frequently recurring value in a range. This tip explains how to use the ...
Discover MoreIf you need to determine the date of the last day in a month, it's hard to beat the flexibility of the EOMONTH function. ...
Discover MoreExcel allows you to easily develop formulas that pull values from worksheets and workbooks other than the one in which ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2022-03-07 23:16:01
Oz
I am AMAZED with those several comments of HATRED towards Progress and Better Program Structure and Usage...
You Obviously Don't Understand the HUGE PROGRESS made here!!!
The 2 Main Advantage, to put in mind, in this Great Leap:
1. Only ONE FORMULA-CELL is to update or change, if needed; Not the whole CSE Range and each of its cells! - Consistency is promised to be kept!
2. It CHANGES SIZE AUTOMATICALLY ("DYNAMICALLY") (expands and reduces), Reacting to the changes and updates in data fed, and in accordance to resulting changes in the Amount of results received!
You better off review those 2 official Microsoft articles:
Dynamic array formulas and spilled array behavior
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dynamic-array-formulas-and-spilled-array-behavior-205c6b06-03ba-4151-89a1-87a7eb36e531
Dynamic array formulas vs. legacy CSE array formulas
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/office/dynamic-array-formulas-vs-legacy-cse-array-formulas-ca421f1b-fbb2-4c99-9924-df571bd4f1b4
Maybe you also want to continue using the cumbersome combination of INDEX-MATCH functions and instead of progressing to the new XLOOKUP function?!
2021-08-06 16:04:40
LS
Spill is yet another example of Microsoft adding features that (for the vast majority of users) are worthless and causing us to figure out how the hell to do things that have worked for decades. It's the number one reason why I held on to my CD copy of Office for as long as I could - there's been nothing added that I needed for many, many versions. IMO, MS just keeps updating it to squeeze more $$s from us. What MS really needs is to release a "lite" version of Excel & Word w/out all the junk they keep adding to it. So frustrating
2021-06-23 10:52:16
J. Woolley
You might be interested in the freely available SpillArray(V_Array) function in My Excel Toolbox. This function is useful in older versions of Excel that do not support dynamic arrays. It will determine and populate the spill range for array expression V_Array, simulating a dynamic array.
The SpillArray function is in module M_RunMacro. The MyToolbox.xlam add-in file includes everything in My Excel Toolbox. See https://sites.google.com/view/MyExcelToolbox/
2021-06-22 07:05:18
Ethel Aardvaard
Backwards compatibility has been a key principle of IT systems since the days of at least the Acorn Atom (and far longer in the Unix world), so for Microsoft to throw it away now is ridiculous.
For me, I have data in cells A1, B1, C1 and E1. I want D1 to be "=CONCATENATE(A1:C1)" but I cannot do this any more because Microsoft has broken the rule of backwards compatibility. Instead, EXCEL has decided that cells E1, F1 and G1 should also contain "=CONCATENATE(A1:C1)" - EXACTLY the same and utterly pointless & useless.
It is NOT acceptable to suggest that I should relearn Excel, after 25+ years of use. Microsoft should NOT implement new "features" in such a poorly-thought out manner.
2020-12-15 09:29:29
Jan
Although I learned to work around this issue, I was recently updated to Excel 2016. And miracle of miracles, the spill error no longer occurs. The vlookup also no longer auto-populates the column, you do need to complete it yourself, but it is sooooo much easier and much less time consuming. The example above may look simple, but I'm working with hundreds of thousands of lines and that spill error was a total annoyance.
2020-09-09 04:22:08
VV
You may say what you want, Spill is not a feature, its a bug and it screws up perfectly working sheets. You have to pay for the SW but M$ wont pay for your extra work. Thank you Microsoft
2020-03-21 09:51:33
Irl
Not to be a curmudgeon, but ... the formula as entered seems very odd. If he later decides he needs to add a few more colors to column E, he couldn't then just Copy Down the formulas in column F because they each reference a fixed range. The formulas in F should just use E2 (or maybe $E2) as first argument, which seems more logical and would avoid the #SPILL error
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2025 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments