Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Generating Unique Numbers for Worksheets.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated February 26, 2022)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365
Sometimes you may need Excel to generate a unique number for your worksheets. For instance, you could be using Excel to create forms such as invoices, statements, or tracking sheets, and you need unique numbers for each form (I'll call this a ticket number). This, of course, implies that Excel needs to remember the number from one session to the next.
There are a couple of ways you can approach this problem. If the numbers don't need to be sequential, you could create a ticket number based on the current time of day, in seconds. The following macro can be added to the ThisWorksheet object:
Private Sub Workbook_NewSheet(ByVal Sh As Object)
Dim lTicket As Long
lTicket = CLng(Time * 24 * 60 * 60)
Sh.Range("A1") = lTicket
End Sub
The macro is triggered every time a new worksheet is added to the workbook. It takes the current time, converts it to an integer number of seconds, and then places that value into cell A1. The likelihood of duplicating ticket numbers within any given day is remote, but it could happen over time. (For instance, if you create a ticket at the exact same time today that you did yesterday or last week.)
To get around this problem, you could create a ticket number in the following manner:
Private Sub Workbook_NewSheet(ByVal Sh As Object)
Dim sTemp As String
sTemp = Format(Date, "yymmdd") & Format(Time, "hhmmss")
Sh.Range("A1") = sTemp
End Sub
This version of the event handler constructs a ticket number based both the date and time. Unless you are creating tickets very quickly, this approach should reduce the possibility of duplicate numbers generated by the macro.
If the numbers must be sequential within the current workbook, then you can define a name that contains the current high value of your ticket number, and then a macro that places that number in a cell on a new worksheet and increments the value of the stored number. Follow these steps to start:
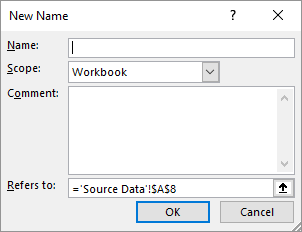
Figure 1. The New Name dialog box.
Now, add the following macro to the ThisWorksheet object in the VBA Editor:
Private Sub Workbook_NewSheet(ByVal Sh As Object)
Dim iMax As Integer
iMax = Mid(ThisWorkbook.Names("MaxNum"), 2)
Sh.Range("A1") = iMax
iMax = iMax + 1
ThisWorkbook.Names("MaxNum").RefersTo = "=" & iMax
End Sub
This macro is executed every time you insert a new worksheet in the workbook. It retrieves the value you stored in the MaxNum, places that value into cell A1 of the new worksheet, and then increments what is stored in MaxNum.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (11192) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Generating Unique Numbers for Worksheets.

Dive Deep into Macros! Make Excel do things you thought were impossible, discover techniques you won't find anywhere else, and create powerful automated reports. Bill Jelen and Tracy Syrstad help you instantly visualize information to make it actionable. You’ll find step-by-step instructions, real-world case studies, and 50 workbooks packed with examples and solutions. Check out Microsoft Excel 2019 VBA and Macros today!
Do you want a way to reverse names within a cell, making them "last, first" instead of "first last?" Here's a handy macro ...
Discover MoreGot a macro that doesn't have quite the right name? You can rename the macro by following these simple steps.
Discover MoreWhen you use a macro to do file operations, it works (by default) within the current directory. If you want to know which ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2022-02-26 12:31:17
J. Woolley
My Excel Toolbox includes the VBA support function GUID_String(). The probability that any single result will be duplicated is negligible.
See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Universally_unique_identifier
See http://www.cpearson.com/Excel/CreateGUID.aspx
See https://sites.google.com/view/MyExcelToolbox/
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments