Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Calculating Business Days.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated February 4, 2023)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365
In performing calculations with Excel, it is often helpful to know how many days there are between two dates. Excel makes this easy—you just subtract the earlier date from the latter.
In a business environment, however, you may not want to know just the number of days—you probably want to know the number of business days between two dates. In other words, how many workdays are there between two dates?
Believe it or not, Excel makes it almost as easy to calculate business days as it is to calculate regular days. All you need to do is use the NETWORKDAYS worksheet function. Let's suppose for a moment that you had two dates: one in A3 and the other in A4. The date in A3 is your starting date and the date in A4 is the ending date. To calculate the work days between the two dates, you could use the following formula:
=NETWORKDAYS(A3,A4)
This returns a count of all the days between the two dates, not counting weekends. You should note that the function returns the number of full days. Thus, if your starting date was Sept. 4 and your ending date was Sept. 5, the function would return a value of 2. (Provided neither day was a weekend day.)
If you want to account for holidays, the easiest way is to enter your standard holidays in a range of cells, and then define a name for that range. (I always like the terribly obvious name of “Holidays.”) You can then alter the NETWORKDAYS formula in this manner:
=NETWORKDAYS(A3,A4,Holidays)
Microsoft also introduced an expanded version of the NETWORKDAYS function in Excel 2010, but it has a different function name: NETWORKDAYS.INTL. The biggest difference between NETWORKDAYS.INTL and NETWORKDAYS is that NETWORKDAYS.INTL allows you to specify how the function should handle weekends. This new parameter goes right after the ending date parameter. So, for instance, if you wanted to know the number of work business days between the dates in A3 and A4 and you wanted to take holidays into account, you would use something like the following:
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL(A3,A4,1,Holidays)
Note the addition of the "1" parameter in the third parameter position. The value you use here can be any of 14 values:
| Number | Weekend Days | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Saturday, Sunday | |
| 2 | Sunday, Monday | |
| 3 | Monday, Tuesday | |
| 4 | Tuesday, Wednesday | |
| 5 | Wednesday, Thursday | |
| 6 | Thursday, Friday | |
| 7 | Friday, Saturday | |
| 11 | Sunday | |
| 12 | Monday | |
| 13 | Tuesday | |
| 14 | Wednesday | |
| 15 | Thursday | |
| 16 | Friday | |
| 17 | Saturday |
If that isn't flexible enough for you, NETWORKDAYS.INTL allows you to use a string for the third parameter that exactly specifies which days should be considered workdays and weekend days. So, for instance, let's say that your company uses a four-day workweek, Monday through Thursday. In this case, you could use a formula such as the following:
=NETWORKDAYS.INTL(A3,A4,"0000111",Holidays)
Note that the string in the third parameter position is exactly 7 digits long and represents the days of the week, Monday through Sunday. A 0 indicates that day is a workday and a 1 indicates it is a "weekend" day that should not be used in calculations.
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (12401) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Calculating Business Days.

Program Successfully in Excel! This guide will provide you with all the information you need to automate any task in Excel and save time and effort. Learn how to extend Excel's functionality with VBA to create solutions not possible with the standard features. Includes latest information for Excel 2024 and Microsoft 365. Check out Mastering Excel VBA Programming today!
Excel allows you to perform quite a few operations using dates in your worksheet. Sometimes, however, the answer may not ...
Discover MoreYou can use a couple of different worksheet functions to enter today's date in a cell. What if you want to calculate ...
Discover MoreGiven a particular week number for a year, you may want to figure out the date of the last day in that week. There is no ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2023-02-06 18:17:08
Tomek
Bob:
Further to my earlier comment:
The macro below will automatically find the end date you wanted, then adjust the date to not fall on a weekend or holiday.
For the purposes of the macro I created named ranges:
(see Figure 1 below)
Target = A2 - that is where you put desired number of workdays. I added this to the sheet so that you can change the number of workdays without changing the macro code.
Start = A3 - your start date
End = A4 - you can put any date there, the macro will adjust it to your burnout date.
Once you put your start date and number of workdays run the macro. If the resulting end date is not a workday, it will ask you if you want to adjust it.
--------------------
Sub FinalDate()
DesiredDays = Range("Target").Value
Range("A5").GoalSeek Goal:=DesiredDays, ChangingCell:=Range("End")
Dim cl As Range
Set cl = Range("End")
If Weekday(cl) = vbSaturday Or Weekday(cl) = vbSunday Or Range("hd") = "Holiday" Then
continue = MsgBox("End date is on weekend or holiday." & vbCr & "Adjust the date?", vbYesNo, "Adjust?")
If continue = vbYes Then
Do
cl.Value = cl.Value - 1
Loop While Weekday(cl) = vbSaturday Or Weekday(cl) = vbSunday Or Range("hd") = "Holiday"
End If
End If
End Sub
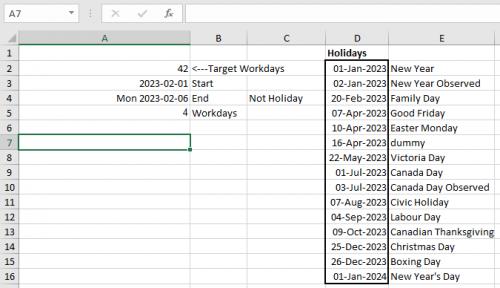
Figure 1.
2023-02-06 17:51:27
Tomek
Bob:
An Excel formula may be a bit complicated for what you need, as there would need to be a circular reference between the end date and Holidays. But there is a way to get what you need:
Use one of the formulas Allen suggested, e.g., =NETWORKDAYS(A3,A4,Holidays) say in the cell A5. Put your start date in cell A3, and any date in cell A4.
Then use the a functionality of Excel called Goal Seek. (Data tab - Forecast Group - What-If-Analysis -Goal Seek). (see Figure 1 below) for what to enter in the fields.
Once you click OK you will get a solution. (see Figure 2 below)
Note that I have a range named Holidays in my spreadsheet, as Allen suggested.
There is a quirk in how the process operates, because the target date found may actually be on a weekend or on a holiday, which technically will be correct, but not necessarily what you want. See, the process uses an algorithm, that is similar to trial and error, and once it finds the date that satisfies the value in the target cell, it does not look any further. This can be relatively easily corrected by manually adjusting the date to an earlier date just before the weekend or holiday (it should result in the same number of workdays). To aid in it, you can format the end date to show the weekday, and add an indicator for holiday in a cell beside it. the formula for the latter could be:
=IF(ISNA(MATCH(A4,Holidays,0)),"Not Holiday","Holiday")
See the figures.
It is worth remembering that the workdays function doesn't count the start day, so if the starting day is today and the end day is tomorrow, it will only return 1 day not 2.
If you need to do this often, you can create a macro to automate both the Goal Seek and the date adjustment. I will post a macro suggestion separately.
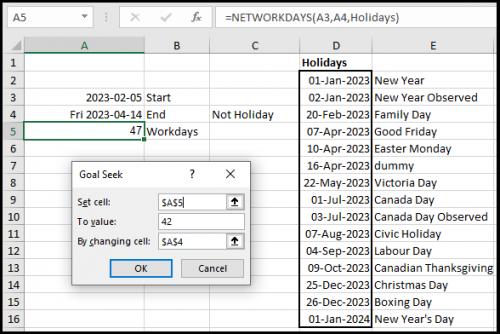
Figure 1.
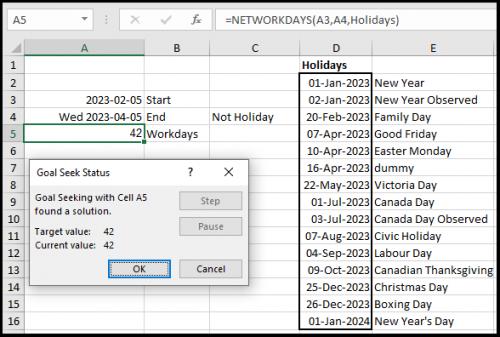
Figure 2.
2023-02-04 15:27:10
Bob Houghton
If I have a start date, and know there are 42 workdays left for a worker, is there a formula that would tell be the burnout date taking into consideration of the weekend days?
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments