Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated September 9, 2024)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021
Shauna understands that she can store macros in her personal workbook so they are accessible anytime she's using Excel. In doing some research, it is unclear to her exactly how this workbook is saved. She has seen references to both Personal.xlsm and Personal.xlsb, so she wonders what the actual name is for the personal workbook and what to do if she finds both the XLSM and XLSB versions on her system.
The personal workbook is, most often, referred to as the "personal macro workbook" because it is used to store macros that you want available at all times in Excel. Macros are only available to use if they are stored in a workbook that is currently open. Thus, if you store a macro in your personal macro workbook, it will always be available because the workbook is always opened, automatically, whenever you start Excel.
This may seem confusing, as you don't normally see the personal macro workbook when you start Excel. That is because it is hidden, by default, so that it doesn't interfere with whatever work you want to do in your other workbooks. The fact that it is hidden is, in fact, the key to discovering if you have a personal macro workbook available on your system. Follow these steps:
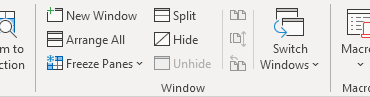
Figure 1. The Unhide tool is not accessible, so there is no personal macro workbook on this system.
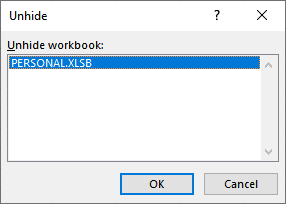
Figure 2. The Unhide dialog box.
As you may have gathered from the above instructions, it is entirely possible that you don't have a personal macro workbook on your system. This is normal; it is only created if you record a macro (or write one from scratch) and specifically tell Excel to store the macro in the Personal Macro Workbook. (See Figure 3.)
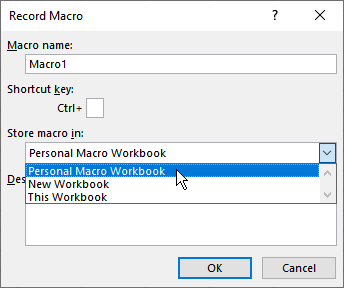
Figure 3. Specifying where to save a macro.
On all modern Excel versions (Excel 2007 and later), when you create a personal macro workbook, Excel does so using the XLSB format. Where the personal macro workbook is stored depends on the version of Excel you are using. The short story is that it is stored in the XLStart folder. (Anything in this folder is automatically loaded when you start Excel, thus the reasoning of putting the personal macro workbook there.) For most of the more modern versions of Excel, the path to the XLStart folder is this:
C:\Users\"your name"\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Excel\XLSTART\
In this path, "your name" is a placeholder for your actual username. Thus, if my username on the system is JDoe, then this would be the path:
C:\Users\JDoe\AppData\Roaming\Microsoft\Excel\XLSTART\
You should note that the AppData folder is hidden, by default. This means that in order to access the folder, you'll need to enable the display of hidden files on your Windows system. You can do that by following this tip, over on the WindowsTips site:
https://windows.tips.net/T011964
If you look in the folder using File Explorer, you'll see the PERSONAL.XLSB workbook, provided one exists on your system. If you see other workbooks in the folder, those workbooks are opened, automatically, when Excel starts (as already mentioned). This leads to an interesting situation. If you see both PERSONAL.XLSB and PERSONAL.XLSM workbooks in the folder, then Excel, when starting, treats PERSONAL.XLSB as your personal macro workbook and opens PERSONAL.XLSM as a regular workbook. Even if you delete PERSONAL.XLSB (so that only PERSONAL.XLSM is in XLStart), Excel will open PERSONAL.XLSM as a regular workbook and consider that you don't have a personal macro workbook available.
The only way that you would see a PERSONAL.XLSM formatted workbook in the XLStart folder is if someone specifically saved a workbook using that name and moved it to the folder.
Tellingly, Excel balks at saving a personal macro workbook in the XLSM format. Assuming you have a personal macro workbook on your system, follow these steps to see what I mean:
At this point, you'll see a familiar question: "Do you want to save the changes in the Personal Macro Workbook?" (You've no doubt seen this question before upon exiting Excel. It appears any time you make changes that affect the personal macro workbook.) If you click the Save button, you'll see a notice that you may have never seen before. (See Figure 4.)
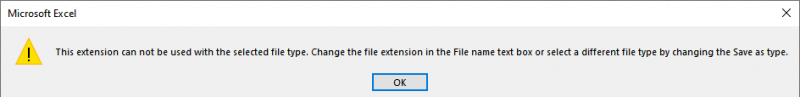
Figure 4. You can't save the personal macro workbook in this format.
This notice is displayed because you are trying to save, for real, the personal macro workbook in the XLSM format, and Excel doesn't like that; it expects it to be in the XLSB format. Click OK a few more times, and you'll eventually get to a new notice. (See Figure 5.)
Figure 5. A new idea for saving in the XLSM format.
If you do, indeed, save the personal macro workbook in a different folder, exit Excel, move it to the XLStart folder, delete PERSONAL.XLSB (so that PERSONAL.XLSM is the only file there), and restart Excel, then (and only then) will you be able to use PERSONAL.XLSM as your personal macro workbook.
Why would you go through all these steps? There is no reason, really. Excel wants to use PERSONAL.XLSB, and it will use PERSONAL.XLSM only if it absolutely has to. Plus, if you go through all the steps so that PERSONAL.XLSM is the only workbook in the XLStart folder, then when you start Excel, the program starts as an "empty shell," without any workbook loaded. It does this because it is actually loading PERSONAL.XLSM, but since it is hidden (as any good personal macro workbook should be), it doesn't display.
The bottom line, to answer Shauna's question, is that the only real personal macro workbook is PERSONAL.XLSB. If you do have a PERSONAL.XLSM on your system, it is there as a fluke or someone went to a lot of trouble to create it. You should move it somewhere else, out of the XLStart folder, and restart Excel. Everything should work normally, and you'll be able to use Excel as you expect, using the files that Excel expects.
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (13810) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021.

Professional Development Guidance! Four world-class developers offer start-to-finish guidance for building powerful, robust, and secure applications with Excel. The authors show how to consistently make the right design decisions and make the most of Excel's powerful features. Check out Professional Excel Development today!
When you change from one worksheet to another, you may want to have Excel automatically run a macro for the worksheet you ...
Discover MoreDo you often need to know the difference between two values in your worksheet? This tip shares a quick little macro that ...
Discover MoreOn your system you may have workbooks that contain macros you know are safe to use. Microsoft provides two things you can ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2020-12-13 18:26:05
Bob Williams
A note about the Workbook_Open routine, which you can put in the ThisWorkbook module of the Personal Macro Workbook (PMW), might be helpful. My effort to do so showed that no code could go in there that assumes that the workbook you are trying to open is already open! E.g., no Named Ranges or built-in variables like ActiveCell or ActiveWindow can be used. (In fact, I'm not sure what useful thing one could do here.)
Also, a comparison of the PMW with a template file would be in order. I frequently fret over where to store often-used bits of code and a template file works for that. (You must have solved such organizational conundrums long since!)
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments