Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Recording a Macro.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated January 27, 2024)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365
If you have a repetitive task that is a good candidate for a macro, you can use the macro recording capabilities of Excel to turn your actions into a macro. To record a macro, follow these steps:
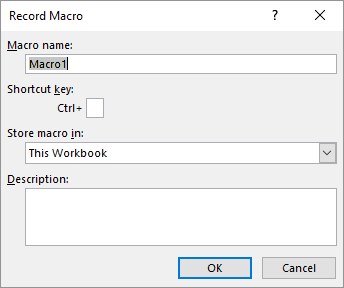
Figure 1. The Record Macro dialog box.
Excel starts recording everything you do. The actions you take become steps in the macro and will be repeated when you later execute the macro. When you have finished the steps you want recorded in your macro, again display the Developer tab of the ribbon and click the Stop Recording tool. (This tool is only available when you are actually recording your macro.) The macro is then saved and available for use at any time.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (5683) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Recording a Macro.

Program Successfully in Excel! This guide will provide you with all the information you need to automate any task in Excel and save time and effort. Learn how to extend Excel's functionality with VBA to create solutions not possible with the standard features. Includes latest information for Excel 2024 and Microsoft 365. Check out Mastering Excel VBA Programming today!
If you keep on-going data in a worksheet, some of your data�"over time�"may need to be deleted. If you have an ...
Discover MoreOne of the powerful programming structures available in VBA is the Select Case structure. This tip explains how you can ...
Discover MoreYou can, from within your macros, easily display a message box containing a message of your choice. If you want to ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2024-01-29 12:16:39
J. Woolley
BARRY mentioned the "Use relative references" function (option) but was vague about how. It is in the Code group of the Ribbon's Developer tab under the Record Macro "tool" discussed in the Tip.
See https://www.excel-easy.com/vba/examples/use-relative-references.html
You might also notice the Record Macro "tool" near the left side of the Status Bar at the bottom of Excel's window. If you don't see it, right-click the Status Bar and press M to enable it (Macro Recording). This makes it easy to start and stop recording, but you still must use the Ribbon's Developer tab to toggle the status of Use Relative References (which is always FALSE when Excel starts).
The status of Use Relative References can be reviewed (but not set) in VBA using the Application.RecordRelative property. My Excel Toolbox includes the following function:
=VBAResult(Expression)
where the text argument is a VBA expression (right side of equal sign). So this cell formula will return the current status of Use Relative References:
=VBAResult("Application.RecordRelative")
See https://sites.google.com/view/MyExcelToolbox/
2024-01-27 07:11:17
BARRY
The macro recorder is a useful tool for those not into VBA. However it's default setting of using absolute addresses can be quite limiting, flipping judicially between that and relative addressing whilst recording the macro greatly improves the usefulness of any macro that you may record.
The "Use relative references" function does this, accessing it depends upon your version of Excel.
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments