Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Using Dynamic Chart Titles.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated July 26, 2024)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021
There is a very cool way, apparently not well known, of adding 'active' or 'live' titles and other text to charts. In this way you can make a change in a worksheet and have that change reflected in a title in the chart. Follow these steps:
=MySheet!$A$1
That's it. Now, whenever the contents of A1 are changed Excel updates the information in the chart's title.
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (9701) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Using Dynamic Chart Titles.

Excel Smarts for Beginners! Featuring the friendly and trusted For Dummies style, this popular guide shows beginners how to get up and running with Excel while also helping more experienced users get comfortable with the newest features. Check out Excel 2019 For Dummies today!
Once you create a chart, you aren't limited to keeping the data series in the order they originally appeared. You can ...
Discover MoreWhen you are working with embedded charts in a workbook, you may want to resize them to a specific size. This tip looks ...
Discover MoreIf you need a number of charts in your workbook to all be the same size, it can be a bother to manually change each of ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2020-08-10 18:41:03
Ronmio
To elaborate on Allen's tip and Dave's suggestion, since Excel only allows a simple "=" pointing to a single cell, you need to get creative in the referenced cell.
[sorry about the duplicates from trying to decipher how to insert an image]
My formulas (hidden behind the graph as Dave suggested) typically use concatenation. For example, by using a couple of helper cells (LargestDate whose formula is =Large(Date,1) and FifthLargestDate whose formula is =Large(Date,5), both also hidden behind the chart), this formula ...
="Daily Volumes (averaging "&AVERAGEIFS(Amount,Date,"<="&LargestDate,Date,">="&FifthLargestDate)&" over the most recent 5 days)"
will produce a dynamic Chart Title (or Axis Name, etc.) that reads like this,
Daily Volumes (averaging 22.6 over the most recent 5 days)
Like Dave, my charts will often contain many expressive chart elements.
Along the same lines, I will add a text box in the chart to create a more expressive "Legend". One big advantage of using a text box within a chart is that you can tailor it extensively (e.g., right clicking on some or all the text to add bullets, condense the line spacing using Paragraph formatting, etc.
(see Figure 1 below)
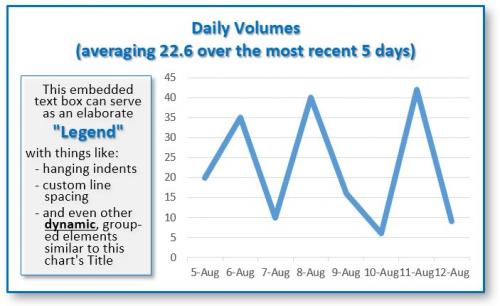
Figure 1.
2020-08-10 11:13:59
Dave
I often skip using Excel's chart and axis titles.
Instead, I use the cells under the chart for these titles.
Why? For more flexibility. I can format the cells any way I want, including coloring some font characters, adding subtitles and all that stuff.
I sometimes even do that for the category axis titles of bar charts. For horizontal bar charts, I use one row for each horizontal bar. For vertical bar charts, I use one column for each vertical bar. It sometimes takes a bit of fiddling, so I save this technique for only where it adds value.
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments