Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Converting an Unsupported Date Format.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated February 12, 2026)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021
It is not uncommon to load information from other programs into Excel. For instance, you may have data generated by another program, and you want to analyze that data in Excel. When you import data into Excel, it does a fairly good job of assigning the proper data types to information, and it can even parse and convert some data.
When it comes to dates and times, however, not all programs speak in a way that Excel can understand. For instance, if your other program stores dates in the format "Mon Jan 13 14:33:03 2011", then Excel won't be able to parse the date and you will need to do the conversion in some other manner.
Fortunately, most programs generate their dates and times in a format that follows a pattern. Assuming, for instance, that "Mon Jan 13 14:33:03 2001" represents the format followed by all dates, you can do the conversion using a simple formula:
=DATEVALUE(MID(A1,9,2)&MID(A1,5,3)&RIGHT(A1,4)) + TIMEVALUE(MID(A1,12,8))
This formula assumes that the foreign date/time format is in cell A1. Simply format the result of the formula using one of Excel's date/time formats, and you'll have no problem.
If you prefer, you can use the Text to Columns function to break the foreign date/time format into its integral parts:
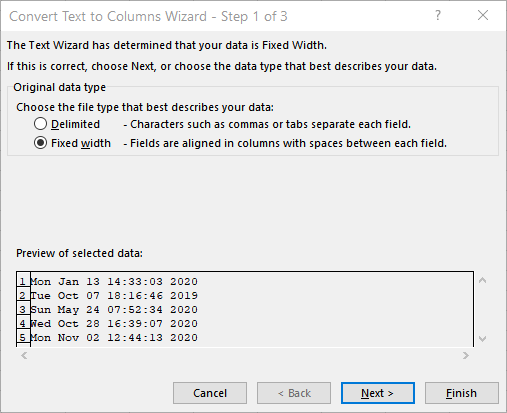
Figure 1. The Convert Text to Columns Wizard.
The dates and times are now separated into five individual columns. You can now use a formula to put a valid date/time back together. For instance, assuming that the exploded version of the date/time is in cells A1:E1, you could use the following:
=(C1&B1&E1)+D2
Again, format the result using a date/time format, and you are all set.
If you prefer to use a macro to do the conversion, then the following macro will step through all the selected cells and do the conversion:
Sub ConvDate()
Dim c As Range
For Each c In Selection.Cells
c = DateValue(Mid(c, 5, 6) & ", " _
& Mid(c, 21, 4)) + TimeValue(Mid(c, 12, 8))
c.NumberFormat = "dd MMMM yyyy h:mm:ss"
Next c
End Sub
The macro converts the text string to an acceptable date/time (using DateValue) and then formats the cell to display the value property.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (9779) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Converting an Unsupported Date Format.

Professional Development Guidance! Four world-class developers offer start-to-finish guidance for building powerful, robust, and secure applications with Excel. The authors show how to consistently make the right design decisions and make the most of Excel's powerful features. Check out Professional Excel Development today!
Need to print an elapsed date in a strange format? It's easier to do than may appear at first glance. Here's a discussion ...
Discover MoreMany businesses organize information according to calendar quarters, especially when it comes to fiscal information. ...
Discover MoreEveryone seems to determine the difference between dates differently. Nicole has a need to calculate contact weeks (the ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2021-04-26 03:05:34
Mark Galloway
Shouldn't the formula "=(C1&B1&E1)+D2" be "=(C1&B1&E1)+D1" ?
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments