Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated September 20, 2023)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021
Ken wonders if there is a worksheet function that will indicate whether the contents of a cell are bold. He can find other informational functions, such as ISBLANK, but cannot find one that will indicate if the cell is bold.
There is no ISBOLD function built into Excel. There is a very arcane way to do this without resorting to a macro, but it only works with some versions of Excel. Apparently, for example, this approach won't work with Office 365, as it appears that Microsoft has finally removed support for it. This old Excel 4 function, called GET.CELL, will work with some older versions of Excel. Here is how you would use it in a formula:
=IF(GET.CELL(20,A1), "Bold", "Not Bold")
The GET.CELL function returns True if at least the first character in the cell is bold.
A better approach would be to create a User-Defined Function in VBA that could be called from your worksheet. Here's a simple version of such a UDF:
Function CheckBold(cell As Range) As Boolean
Application.Volatile
CheckBold = cell.Font.Bold
End Function
In order to use it in your worksheet, you would do so in this manner:
=IF(CheckBold(A1), "Bold", "Not Bold")
The CheckBold function will only update when your worksheet is recalculated, not if you simply apply bold formatting to or remove it from cell A1.
This approach can work for most instances but understand that the Bold property can actually have three possible settings—True, False, and Null. The property is set to False if none of the characters in the cell are bold. It is set to True if they are all bold. Finally, it is set to Null if only some of the characters in the cell are bold. If you think you might run into this situation, then you'll need to modify the CheckBold function:
Function CheckBold(cell As Range) As Integer
Dim iBold As Integer
Application.Volatile
iBold = 0
If IsNull(cell.Font.Bold) Then
iBold = 2
Else
If cell.Font.Bold Then iBold = 1
End If
CheckBold = iBold
End Function
Note that the function now returns a value, 0 through 2. If it returns 0, there is no bold in the cell. If it returns 1, then the entire cell is bold. If it returns 2, then there is partial bold in the cell.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (13733) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021.

Program Successfully in Excel! This guide will provide you with all the information you need to automate any task in Excel and save time and effort. Learn how to extend Excel's functionality with VBA to create solutions not possible with the standard features. Includes latest information for Excel 2024 and Microsoft 365. Check out Mastering Excel VBA Programming today!
There are some numbers that require leading zeros, such as ZIP Codes. Excel provides several different ways that you can ...
Discover MoreExcel often changes the formatting of a cell based on how it parses what you are entering into that cell. This is ...
Discover MoreThere are many ways that Excel allows you to highlight information in a cell. This tip examines a way to highlight values ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2020-10-11 12:04:18
Kell Vagtholm
Hi
Is it possible to create a cell formulat like =SUM(A2:A8), including some kind of check so that only cell values in Bold will be summed?
Best regards,
Kell Vagtholm
2020-04-14 09:26:58
R Monat
Correction :
...The "$" before "B" prevents the column from indexing...
Addition:
Cell B8 is evaluated for whether it is bold or not.
2020-04-14 09:23:32
R Monat
It works in Office365 by setting the get.cell function to the range definition (make sure you have selected the correct cell to start with). This image shows the function being used when cell D8 is selected on sheet "ProjectSchedule". The "$" before "D" prevents the column from indexing and the absence of the "$" before the "8" allows the row to index. (see Figure 1 below)
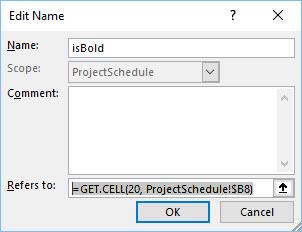
Figure 1. Named Range Definition
2020-02-04 13:45:54
J. Woolley
@Roy
Here is an interesting reference regarding your point about the use of Excel 4 Macro Functions: https://exceloffthegrid.com/using-excel-4-macro-functions/
2020-02-03 16:03:20
Roy
It works just fine in Office 365 (Version 1912, Build 12325.20344 Click-to-Run).
To use Excel 4's macro language functions, you must put the actual formula that uses them in a Named Range. Usually you'd put just the portion that uses one of those functions and use the Named Range appropriately in the spreadsheet-side formula (what you enter in the cells themselves), but this one does only the one thing in the above formula, so why not put the whole thing into the Named Range?
In any case, perhaps your Named Range is "horsey". If soi, you'd put Mr. Wyatt's formula (which works nicely done properly here) into the Named Range, then in the cell you wish to have the result, place "=horsey" and you're done.
Naturally, if you don't use $A$1, but rather the A1 (no dollar signs) used above, you had best choose carefully what cell you have selected when you create the Named Range. Relative referenceing is awesome, but a stonecold ***** when you forget about using it...
Remember, the key is that the ACTUAL Excel 4 macro functions HAVE TO BE in a Named Range. They WILL NOT WORK cell-side. You put them in Named Ranges, then use the Named Ranges cell-side.
EVALUATE() gets the most press, but all the GET.xxx() functions can be hideously useful. There are at least a half dozen others of interest. Even those that seem in the modern set of functions sometimes behave differently in meaningful ways. Which tweaks my mind to check about a problem I currently have with a "modern" function.
Some evidence suggests that MS can NEVER ditch these functions no matter how much they suggest it could happen anytime (which they have been saying for 25 years...). A fairly complete rewrite of Excel would be one instance of how they could do so someday but unless the mobile version of Exxcel is a complete rewrite, hence it big differences from the desktop program, maybe the MOBILE version cannot use these anymore. Maybe. My bet is it still can and will continue to be able to for decades. 'Cause MS doesn't seem... into... the idea of a complete, modernizing, rewrite.
2020-02-01 15:49:26
John Mann
I tried the GET.CELL function in Excel 10, and it didn't work, got "That function is not valid"
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments