Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated March 22, 2021)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021
Roger has a worksheet column that contains a list of sculptures. He needs a simple way to count up the number of occurrences of "mouse" or "dragonfly," but it's not always the only text in the cell. He can't find any "COUNTIF-CONTAINS" function, and he can do it manually using Find and Replace, but figures there has to be a better way.
There are actually multiple ways you can approach this issue. One easy way is to use filtering to show only the rows that contain the word you want. You can do that by following these steps:
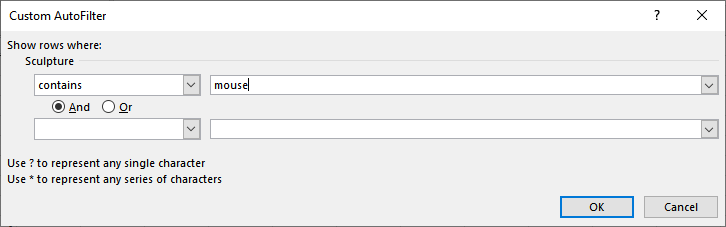
Figure 1. The Custom AutoFilter dialog box.
At this point you can, if there are not too many rows, simply count the rows displayed.
If you would rather use an outright formula, you could rely on the COUNTIF function. This approach works because Excel lets you use wildcards in what you search for in the function. Let's say that you put what you are searching for into cell E1 and you want to search for all instances of rows containing "mouse" in column A. This is the formula to use:
=COUNTIF(A:A,E1)
The trick is to put this text into cell E1: *mouse*. The asterisks are the wildcards, which means that COUNTIF will count any rows that contain at least one instance of the letters "mouse" with anything surrounding those characters.
There are other formulas you could use as well, such as the following:
=COUNT(SEARCH(E1,A:A)) =SUMPRODUCT(IF(IFERROR(SEARCH(E1,A:A)>0*1,0),1,0)) =SUM(IF((ISNUMBER(SEARCH(E1,A:A))),1,0))
When using any of these formulas, you don't need the asterisks surrounding the value in E1; they don't use (or need) wildcards. Also be aware that in some versions of Excel you may need to enter these as array formulas, using Ctrl+Shift+Enter. (You don't need to do this if you are using the version of Excel provided with Microsoft 365.)
You should be aware that any of the formulas presented so far (as well as the filtering approach) have two drawbacks. First, they will count "containing words." This simply means that if you are searching for "mouse," then a word containing "mouse" (such as "mousepad") will count as a match. Second, if the cell contains two instances of what you are searching for (such as "My mouse is your mouse"), then it still only counts as one instance.
If you don't want to run into these types of instances, then the best approach is to create your own user-defined function to do the counting for you. Here's one that is compact and can perform the count:
Function HowMany(rSource As Range, sWord As String) As Long
Dim X As Long
Dim V As Variant
Dim Arr As Variant
Dim sSearch As String
Const Pat As String = "[!A-Za-z0-9]"
Arr = rSource.Value
If VarType(Arr) < 8192 Then Arr = Split(rSource.Value & " ")
sSearch = Pat & LCase(sWord) & Pat
For Each V In Arr
V = " " & LCase(V) & " "
For X = 2 To Len(V) + 1
If Mid(V, X - 1, Len(sWord) + 2) Like sSearch Then
HowMany = HowMany + 1
End If
Next
Next
End Function
In your workbook you would enter the following:
=HowMany(A:A,"mouse")
When using the function on an entire column like this, it can take a while for the function to return. In other words, it can be slow. You would be better served if you specify a range in the function call that contains just the cells you need to search, instead of the entire column.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (13837) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021.

Program Successfully in Excel! This guide will provide you with all the information you need to automate any task in Excel and save time and effort. Learn how to extend Excel's functionality with VBA to create solutions not possible with the standard features. Includes latest information for Excel 2024 and Microsoft 365. Check out Mastering Excel VBA Programming today!
Need to figure out if a value is outside of some arbitrary limit related to a different value? There are a number of ways ...
Discover MoreIf you need to make everything in a cell lowercase except the first character, you may wonder if there is a formulaic way ...
Discover MoreLooking for a formula that can return the address of a cell containing a text string? Look no further; the solution is in ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2021-03-23 14:09:08
Willy Vanhaelen
IMHO this issue can only be solved by a User Defined Function. Here is a shorter version:
Function HowMany(Rng As Range, sWord As String) As Long
Dim Cell As Variant, X As Long
For Each Cell In Rng
Cell = Split(Cell)
For X = 0 To UBound(Cell)
If Cell(X) = sWord Then HowMany = HowMany + 1
Next
Next
End Function
2021-03-22 13:46:17
neil
You could just do a FIND ALL (Ctrl+F then click Find All) for the word you want. It will tell you how many cells contain the text you specify. This method also does not need wildcard asterisks and will find "containing words". if the text appears in a cell more than once, the cell will only be counted once. (see Figure 1 below)
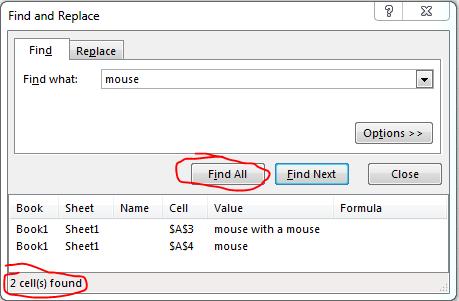
Figure 1. Find All
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments