Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated November 25, 2023)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365
Hanna has a bunch of workbooks that she inherited from others in her company. In the various worksheets in these workbooks, there are a large number of cells that appear empty but aren't really empty. Instead, the cells contain one or two spaces. Hanna wonders if there is a way to quickly delete the contents of such cells.
You could use Find and Replace to accomplish this task. Here are the two general steps you would follow:
This approach works great, unless the data in your worksheet has cells that contain multiple spaces either before the first character in the cell or between characters in the cell. In that case, those multiple spaces will be reduced to a single space, but you may not want that to happen. It is best, then, to use a macro-based approach:
Sub CleanSheet()
Dim rCell As Range
Dim rText As Range
Set rText = Cells.SpecialCells( _
xlCellTypeConstants, xlTextValues)
For Each rCell In rText
If Trim(rCell.Value) = "" Then
rCell.ClearContents
End If
Next
Set rText = Nothing
Set rCell = Nothing
End Sub
The macro checks only cells containing constants (which includes all text in the worksheet) and then checks to see if using the Trim function would result in an empty cell. If so, then the cell is cleared. If the Trim function wouldn't result in an empty cell, then no change is made to the cell.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (5843) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365.

Program Successfully in Excel! This guide will provide you with all the information you need to automate any task in Excel and save time and effort. Learn how to extend Excel's functionality with VBA to create solutions not possible with the standard features. Includes latest information for Excel 2024 and Microsoft 365. Check out Mastering Excel VBA Programming today!
If you type information into a workbook, you may want to make sure that what you type is always stored in uppercase. ...
Discover MoreWhen you copy a worksheet and then need to make changes to information in that worksheet (such as changing month names), ...
Discover MoreWhen entering data in a worksheet, you may only want to add information to the cells in a particular range. You can ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2025-06-01 08:25:05
sandeepkothari
Wow!
2023-11-30 16:02:01
J. Woolley
After my latest comment below, I realized there was no reason to clear a hyperlink from a null cell; it is only necessary to clear the text (making it blank). So the ClearNullCells macro in My Excel Toolbox has been updated accordingly.
The CleanSheet2 and CleanSheet3 macros in my earlier comment should also be changed. Locate the following statement in each
If sTrim = "" Then rMerg.ClearContents
and replace it with this statement
If sTrim = "" Then rMerg.Value = ""
Previously I wasn't aware the Range.ClearContents method also clears hyperlinks.
2023-11-29 12:17:24
J. Woolley
A null cell is one that contains only space characters (Unicode 32 or 160).
My Excel Toolbox now includes the ClearNullCells macro to clear all null cells (making them blank). Merged and/or hidden cells apply. Cells containing formulas are ignored. When a null cell is cleared, its format is not modified; any comment remains, but a hyperlink does not.
There are three options:
1. Clear null cells from all worksheets in all open workbooks
2. Clear null cells from all worksheets in the active workbook
3. Clear null cells from the active worksheet only
See https://sites.google.com/view/MyExcelToolbox/
2023-11-26 14:14:52
J. Woolley
@Craig Buback and Andy
Thanks for the debug assist. Here are updated versions of CleanSheet2 and CleanSheet3. Let me know if you find other issues.
Sub CleanSheet2()
Dim rCell As Range, rText As Range, rMerg As Range, sTrim As String
On Error Resume Next
Set rText = Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants, xlTextValues)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not (rText Is Nothing) Then
For Each rCell In rText
Set rMerg = rCell.MergeArea
If rCell.Address = rMerg.Cells(1).Address Then
sTrim = Trim(Replace(rCell.Value, Chr(160), " "))
If sTrim = "" Then rMerg.ClearContents
End If
Next rCell
End If
End Sub
Sub CleanSheet3()
Dim WB As Workbook, WS As Worksheet
Dim rUsed As Range, rText As Range, rCell As Range, rMerg As Range
Dim nWB As Long, nWS As Long, nC As Long, sTrim As String
Dim nWBX As Long, nWSX As Long, nWBC As Long, nWSC As Long
For Each WB In Workbooks
nWB = nWB + 1: nWBX = nC
For Each WS In WB.Worksheets
nWS = nWS + 1: nWSX = nC
Set rUsed = WS.UsedRange
On Error Resume Next
Set rText = rUsed.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants, xlTextValues)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not (rText Is Nothing) Then
For Each rCell In rText
Set rMerg = rCell.MergeArea
If rCell.Address = rMerg.Cells(1).Address Then
sTrim = Trim(Replace(rCell.Value, Chr(160), " "))
If sTrim = "" Then rMerg.ClearContents: nC = nC + 1
End If
Next rCell
Set rText = Nothing
End If
If nWSX < nC Then nWSC = nWSC + 1
Next WS
If nWBX < nC Then nWBC = nWBC + 1
Next WB
MsgBox nC & " null cells containing only space characters" & vbNewLine _
& "have been cleared from " & nWSC & " of " & nWS & " worksheets" _
& vbNewLine & "in " & nWBC & " of " & nWB & " open workbooks."
End Sub
2023-11-25 14:55:08
Andy
What about the dreaded character code 160 spaces? If any of the contents of the worksheet were sourced from the web, they may not be regular spaces. I have been caught out by this before.
2023-11-25 13:11:26
Craig Buback
The CleanSheet macro returns an error on my sheet which contained merged cells
2023-11-25 11:29:20
J. Woolley
The CleanSheet2 macro in my previous comment below avoids the error discussed there. But Hanna "has a bunch of workbooks" with "various worksheets" to clean. This version will check all worksheets in all open workbooks and report the number of cells modified. It also treats non-break space Chr(160) the same as standard space.
Sub CleanSheet3()
Dim WB As Workbook, WS As Worksheet
Dim rUsed As Range, rText As Range, rCell As Range, nbr As Long
For Each WB In Workbooks
For Each WS In WB.Worksheets
Set rUsed = WS.UsedRange
On Error Resume Next
Set rText = rUsed.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants, xlTextValues)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not (rText Is Nothing) Then
For Each rCell In rText
If Trim(Replace(rCell.Value, Chr(160), " ")) = "" Then
rCell.ClearContents
nbr = nbr + 1
End If
Next rCell
Set rText = Nothing
End If
Next WS
Next WB
MsgBox "In all worksheets of all open workbooks, " & nbr _
& " null cells containing only space characters have been cleared."
End Sub
For more about Range.SpecialCells, see my recent comment here: https://excelribbon.tips.net/T012552_Skipping_Hidden_Rows_in_a_Macro.html
2023-11-25 10:58:13
J. Woolley
The Tip's macro has an issue. If the active worksheet has no text constants, the macro's result will be an error message. Maybe that is an acceptable result. (see Figure 1 below)
Perhaps nobody will run the macro unless the worksheet has text, but that text might be the result of formulas instead of constants. In this case, the result will be the same error message.
Here is a modified version of the Tip's macro that avoids the error:
Sub CleanSheet2()
Dim rCell As Range, rText As Range
On Error Resume Next
Set rText = Cells.SpecialCells(xlCellTypeConstants, xlTextValues)
On Error GoTo 0
If Not (rText Is Nothing) Then
For Each rCell In rText
If Trim(rCell.Value) = "" Then rCell.ClearContents
Next rCell
End If
End Sub
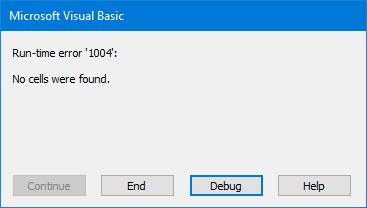
Figure 1.
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments