Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Finding the Size of a Workbook.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated October 1, 2022)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365
Mike wonders if there is a worksheet function that will show him the size, in bytes, of a workbook without using a macro.
The size of a workbook in Excel can become very large, depending on the information it contains. Keeping track of the size is important and can be accomplished a couple of different ways.
If you don't want to use a macro, Excel keeps track of various pieces of information about a file in the Properties dialog box. How you display the dialog box depends on the version of Excel you are using. If you are using Excel 2010 or Excel 2013, follow these steps:
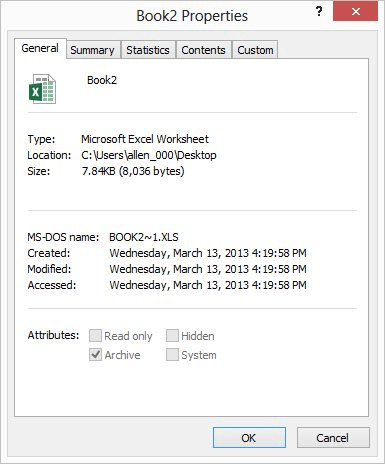
Figure 1. The General tab of the Properties dialog box.
If you are using Excel 2007, follow these steps instead:
In the General tab, Excel displays the size of the file. You will also see other information about the file in this tab including the type of file and who created it. Manually obtaining the file size is simple using this process, but it does not allow you to see the workbook size on the worksheet itself. Unfortunately, there is no way around it; you will need to use a macro. The following is a good example of one you could use:
Function wbksize()
myWbk = Application.ThisWorkbook.FullName
wbksize = FileLen(myWbk)
End Function
To use this macro within a worksheet, just type the following in any cell:
=wbksize()
The file size is displayed in bytes.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (8030) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, and Excel in Microsoft 365. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Finding the Size of a Workbook.

Dive Deep into Macros! Make Excel do things you thought were impossible, discover techniques you won't find anywhere else, and create powerful automated reports. Bill Jelen and Tracy Syrstad help you instantly visualize information to make it actionable. You’ll find step-by-step instructions, real-world case studies, and 50 workbooks packed with examples and solutions. Check out Microsoft Excel 2019 VBA and Macros today!
Delimited files are often created through Excel so that your data can be exported to other programs. If the delimited ...
Discover MoreIt is often necessary to import information from other programs into Excel. Sometimes this can lead to challenges, such ...
Discover MoreWhen you import information from a CSV text file, Excel formats the data according to its default settings. Wouldn't it ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2022-10-03 09:01:33
J. Woolley
My Excel Toolbox includes the function VBAResult(Expression), where the text argument is a VBA expression (right side of equal sign). For example, this cell formula will return the last saved size of the active workbook in bytes:
=VBAResult("FileLen(ActiveWorkbook.FullName)")
See https://sites.google.com/view/MyExcelToolbox/
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments