Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Handling Leading Zeros in CSV Files.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated December 1, 2025)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021
John wrote concerning a problem with handling leading zeros in CSV files. He creates CSV files destined for import into an accounting program but has problems with the CSV files if he needs to first reload the CSV into Excel to correct any mistakes in the file.
Actually, there are two things that need to be checked here. First, is Excel putting the leading zeros in the CSV file it initially creates? Second, is it maintaining the zeros in the CSV file when you reload it and then resave it? These are two separate issues.
You can check the first issue easily enough. All you need to do is rename the CSV file so it has a TXT extension, then you can load it into a text editor, such as Notepad. There you can examine the actual CSV file, as created by Excel, to make sure that everything is in the format you expect. If it is not—for instance, there are no leading zeros where you need them—then you need to be concerned with how Excel is creating the CSV file in the first place.
You need to check whether there are leading zeros in the original Excel information. If there are, and they are displayed, then you need to make sure that the column in which the data is contained is formatted as Text in the Number tab of the Format Cells dialog box. If they are not, then you need to format the cells using a Custom number format that displays the zeros. In both of these cases, the leading zeros will be included in the CSV file created by Excel.
This brings us to the second issue. When you load a CSV file into Excel, it tries to determine the format of the data being loaded. You probably noticed when you loaded your CSV file in Notepad that even though Excel includes leading zeros in the output file, there are no quotes around the field itself. This means that Excel automatically recognizes the field as a number when importing it. By default, then, the number is displayed using one of the number fields, thereby expunging any leading zeros in what Excel displays.
The way around this problem should be fairly obvious based on information earlier in this tip—somehow you need to get Excel to recognize the incoming information as text so that it treats the leading zeros as significant. The quickest way to do this is to follow these steps, prior to loading the CSV file:
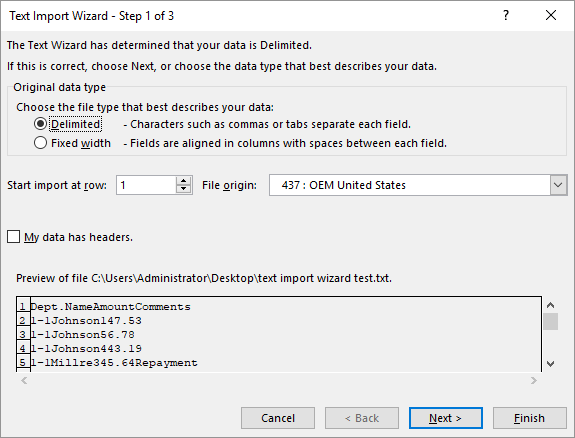
Figure 1. The Text Import Wizard.
Now you can do your work in Excel, as desired, and again save your data in CSV format. (You will, however, need to use Save As rather than simply using Save.) The leading zeros will be included in the data that is saved.
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (10262) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, and 2021. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Handling Leading Zeros in CSV Files.

Program Successfully in Excel! This guide will provide you with all the information you need to automate any task in Excel and save time and effort. Learn how to extend Excel's functionality with VBA to create solutions not possible with the standard features. Includes latest information for Excel 2024 and Microsoft 365. Check out Mastering Excel VBA Programming today!
When processing plain text files in a macro, it is often helpful to know how much data the file contains. The normal way ...
Discover MoreNeed to know what the full path name is for the current workbook? With a simple macro you can display the full path name ...
Discover MoreYou can use Excel for all types of data processing. You may want to work with filenames in a worksheet, but the first ...
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2020-06-20 20:19:00
Roy
Excel examines the first eight records of each field when importing and decides how to treat the column based upon that examination. That can be changed, but... amongst ofhter things, telling it to examine all the rows, say, could mean examining, say, a million records for each of, say, 30 fields... multiplies up, eh? And if none of your rows has characters like you need for the desired effect, it was pointless. One can open in Notepad, say, then insert patterned rows at the start (eight), then delete them after import though. But no one's USER is going to do any part of that, so those records would stay in.
Breaking the file association helps YOU, but only sometimes. I have files I want to import carefully, ones I simply want to open and overwrite, and some that the data in them isn't hurt by this, and the appearance, if it were somehow important (and it can be, though for me the importance is in the output spreadsheet which is already formatted for the material I move over), can be restored with a couple, not fifty, formatting changes. But no USER is ever going to be good with this. But mostly, break the association and you then have to hand-import everything.
Power Query (PQ) is a terrific thing, but it has its own problems, never touted by its proponents, nor even acknowledged. I can't set up a query, then apply it easily to a file with a different name from the one used. Rename the import files to that? Great... unless the currently named "that" is still in use by one or more Users. Hold off until some graet moment? Someone might use old data, or one of the "still in use by" Users might unknowingly use the new data which can lead to action/inaction issues. Think of a spreadhseet used for A/P calls, for example.
Worse, PQ has... its own "I know best" preferences. It like to essentially do a Paste|Special|Values with all formatting changed to Text. Likes may not be a strong enough word. And "essentially" is not fully accuraet: not just the all formatting changed to Text thing, but it also does Precision As Displayed (PAD) unless you override that. That is a HARD thing to notice with more than a wee bit af data being imported until solving some major problem gives you the go-ahead to really delve into it. Like I mentioned above, no one (in the "PQ is awesome, I even use it to cut my hair and boil pasta" camp) talks about it either, so it's a learn-by-screwing-up kind of thing. The fact you're trying to not work with the details —automating something — makes it easy to not worry about things too. It seriously does not want to import formulas, though that is not a problem with CSV material, of course, just a broader issue with PQ.
Easy to overcome all, they say, and it is, if you put the work into it AND have warning of all these things and more so you know the work to do, but... then you're right back to the problem that it is only for THAT data source, i.e., the filename you worked with and one has the issue from above. I'm not even aware of any way to set a preference for each of the import issues I've seen, or even some of them. Once again, like with simple CSV import, MS knows best, MS knows all, MS, like honeybadger, "don't care."
Sad as it is, writing your own import macros is really the only "industrial" (vs. "limping along from one battle to the nmext") solution. And if your organization dislikes macros, well, maybe some Indian company would like to open a new line of support service you could subscribe to.
Second alternative? Muddle through, put out the fires that arise. Each day. Take your lumps in meeting when you get blamed for everything. Accept that whipping boys don't get raises or promotions. And enjoy your vacation leaving the company-paid cellphone at home, whether they like that or not. (They expect you to take it along, and respond, but somehow, being paid for that day and saving the vacation day, does not logically follow...)
2020-05-09 10:03:42
Mark
Alex B's comment about doing this a lot of this is good.
I'd suggest another approach - Power Query. One of the great strengths of Power Query is that it works by recording your steps so you can have it repeat them on each new dataset. And if they need adjustment you can modify them as needed. And finally having a recording of them provides both an audit trail of the data manipulations and a way to share the process with others.
Note that in newer versions of Excel this is on the Data tab in Get & Transform Data to create them and in Queries & Connections to maintain them.
2020-05-09 09:39:25
Jeff Newman
two other ways around this are
1 duplicate the first data line and put alpha characters in the needed field. delete after import
2 many medical fields have leading zeros, but also characters in the same field
find one of these rows and make it the first data row. no deletion is necessary
2020-05-09 08:41:28
Alex B
To open the file in Notepad you don’t need to change the file extension. Just right click on the file and select “Open With” and then select Notepad.
If you then copy the text into excel from notepad you can access the conversion wizard using Data > Text to columns.
If you are doing a lot of this consider breaking the association between the csv file type and excel. If you change the association to say Notepad double clicking the file will open it in Notepad and in excel file open will launch the wizard.
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2026 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments