Please Note: This article is written for users of the following Microsoft Excel versions: 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 2024, and Excel in Microsoft 365. If you are using an earlier version (Excel 2003 or earlier), this tip may not work for you. For a version of this tip written specifically for earlier versions of Excel, click here: Searching for All.
Written by Allen Wyatt (last updated November 1, 2025)
This tip applies to Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 2024, and Excel in Microsoft 365
Jack wonders how he can do a search for a certain word or phrase and, in one step, highlight all the cells containing it so that he can cut or copy them and paste them elsewhere.
Selecting the cells containing the text you want to use is rather easy; you can use the standard Find and Replace feature to do it. Follow these steps:
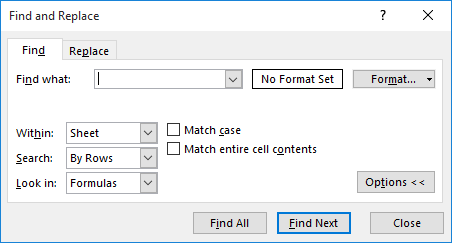
Figure 1. The Find tab of the Find and Replace dialog box.
That's it. As long as you didn't click on Match Entire Cell Contents in step 4, Excel selects all the cells that contain the text you specified in step 3. You can, at that point, apply formatting to the cells, if desired.
You could, of course, use conditional formatting to dynamically format cells that contain the text you want to highlight. All you need to do is set up a condition that uses "Text Contains" as the test. This won't, of course, select all the cells that contain the text, but it will highlight them so you can pick out where they are.
You could also use a macro to select all the cells that contain the desired text. The following is a rather simple one that accomplishes the task:
Sub selCellbasedonValue()
Dim c As Object
Dim u As Range
Dim v As Range
Dim sInpt As String
Set u = ActiveSheet.UsedRange
sInpt = InputBox("Enter the search text")
If sInpt > "" Then
For Each c In u
If Instr(LCase(sInpt),LCase(c.Value)) > 0 Then
If v Is Nothing Then
Set v = Range(c.Address)
Else
Set v = Union(v, Range(c.Address))
End If
End If
Next
v.Select
Set v = Nothing
End If
Set u = Nothing
End Sub
There is a problem with selecting cells that you need to recognize, however—if the cells are non-contiguous, you cannot cut or copy the cells. If you try, you'll get an error message indicating that the command cannot be used on multiple selections. The easiest way to copy cell contents to a different location is to, again, use a macro:
Sub CopyFinds()
Dim sSrch As String
Dim sFirst As String
Dim rPaste As Range
Dim i As Integer
Dim iLeftC As Integer
Dim lTopR As Long
Dim c As Object
If Selection.Cells.Count = 1 Then
MsgBox "Select the range to be searched."
Exit Sub
End If
'Specify search string
sSrch = InputBox(Prompt:="Enter the search text")
' Set the paste address
On Error Resume Next
Set rPaste = Application.InputBox(Prompt:="Enter the upper-left " & _
"cell address for the paste range", Type:=8)
On Error GoTo 0
' Exit if canceled
If TypeName(rPaste) <> "Range" Then Exit Sub
' Upper left cell to be used
Set rPaste = rPaste.Range("A1")
'Set where paste will start and headings
Application.ScreenUpdating = False
lTopR = rPaste.Row
iLeftC = rPaste.Column
Cells(lTopR, iLeftC) = "Address"
Cells(lTopR, iLeftC + 1) = "Cell Value"
lTopR = lTopR + 1
'Start copying cell values
With Selection
Set c = .Find(What:=sSrch, LookAt:=xlPart, MatchCase:=True)
If Not c Is Nothing Then
sFirst = c.Address
Do
Cells(lTopR, iLeftC) = c.Address
Cells(lTopR, iLeftC + 1) = c.Value
Set c = .FindNext(c)
lTopR = lTopR + 1
Loop While Not c Is Nothing And c.Address <> sFirst
End If
End With
Application.ScreenUpdating = True
Cells(rPaste.Row, rPaste.Column).Select
End Sub
When you select a range of cells and run this macro, you are asked to specify what you are searching for (case is important) and an address of where you want to copy it. The macro then finds all cells that contain that value and copies both their address and the cell value to the starting address you specified. The macro doesn't do a lot of error checking; it will overwrite information if you specify a target address that has information in it already. In addition, if you specify a target address that is within the range you are searching, the macro may run infinitely. You should definitely specify a target that is outside of the range being searched.
Note:
ExcelTips is your source for cost-effective Microsoft Excel training. This tip (8964) applies to Microsoft Excel 2007, 2010, 2013, 2016, 2019, 2021, 2024, and Excel in Microsoft 365. You can find a version of this tip for the older menu interface of Excel here: Searching for All.

Dive Deep into Macros! Make Excel do things you thought were impossible, discover techniques you won't find anywhere else, and create powerful automated reports. Bill Jelen and Tracy Syrstad help you instantly visualize information to make it actionable. You’ll find step-by-step instructions, real-world case studies, and 50 workbooks packed with examples and solutions. Check out Microsoft Excel 2019 VBA and Macros today!
If you have a lot of text in your workbook, at some point you might want to split out sentences into individual cells. ...
Discover MoreAs you make edits in Excel, the program remembers your actions so that you can later undo them. If you have multiple ...
Discover MoreWant to select only the formulas in your worksheet? It's easy to do using the Go To Special dialog box.
Discover MoreFREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
2025-11-04 00:37:56
Tomek
Re: There is a problem with selecting cells that you need to recognize, however—if the cells are non-contiguous, you cannot cut or copy the cells. If you try, you'll get an error message indicating that the command cannot be used on multiple selections.
While this is generally true, there is an exception to this: If the non-contiguous selection forms a rectangular pattern with blocks of cells aligned horizontally and vertically and the blocks have the same width and height [{fig}] , such selection can be copied. When pasted, the unselected rows and columns are ignored and the selected cells are pasted as one block.
2025-11-01 06:50:21
Alex Blakenburg
1) Just an FYI - the first method using Ctrl + F and the first macro do a case insensitive search. The 2nd Macro does a case sensitive search. Change "MatchCase:=True" to "MatchCase:=False" if you want it to mimic the other 2 results.
2) The 1st Macro is potentially going to be quite slow. It is likely that it would be faster to load the UsedRange to an array, perform the Instr test on the array and then Union the identified cell.
3) in the 2nd Macro the line "Loop While Not c Is Nothing And c.Address <> sFirst" is what is used in the MS documentation but if c is Nothing the line will still try to perform the address check and the code will error out. In this case we are not changing c so to get to here c will never be nothing and the line only needs to be "Loop While c.Address <> sFirst"
Got a version of Excel that uses the ribbon interface (Excel 2007 or later)? This site is for you! If you use an earlier version of Excel, visit our ExcelTips site focusing on the menu interface.
FREE SERVICE: Get tips like this every week in ExcelTips, a free productivity newsletter. Enter your address and click "Subscribe."
Copyright © 2025 Sharon Parq Associates, Inc.
Comments